You have no items in your shopping basket.
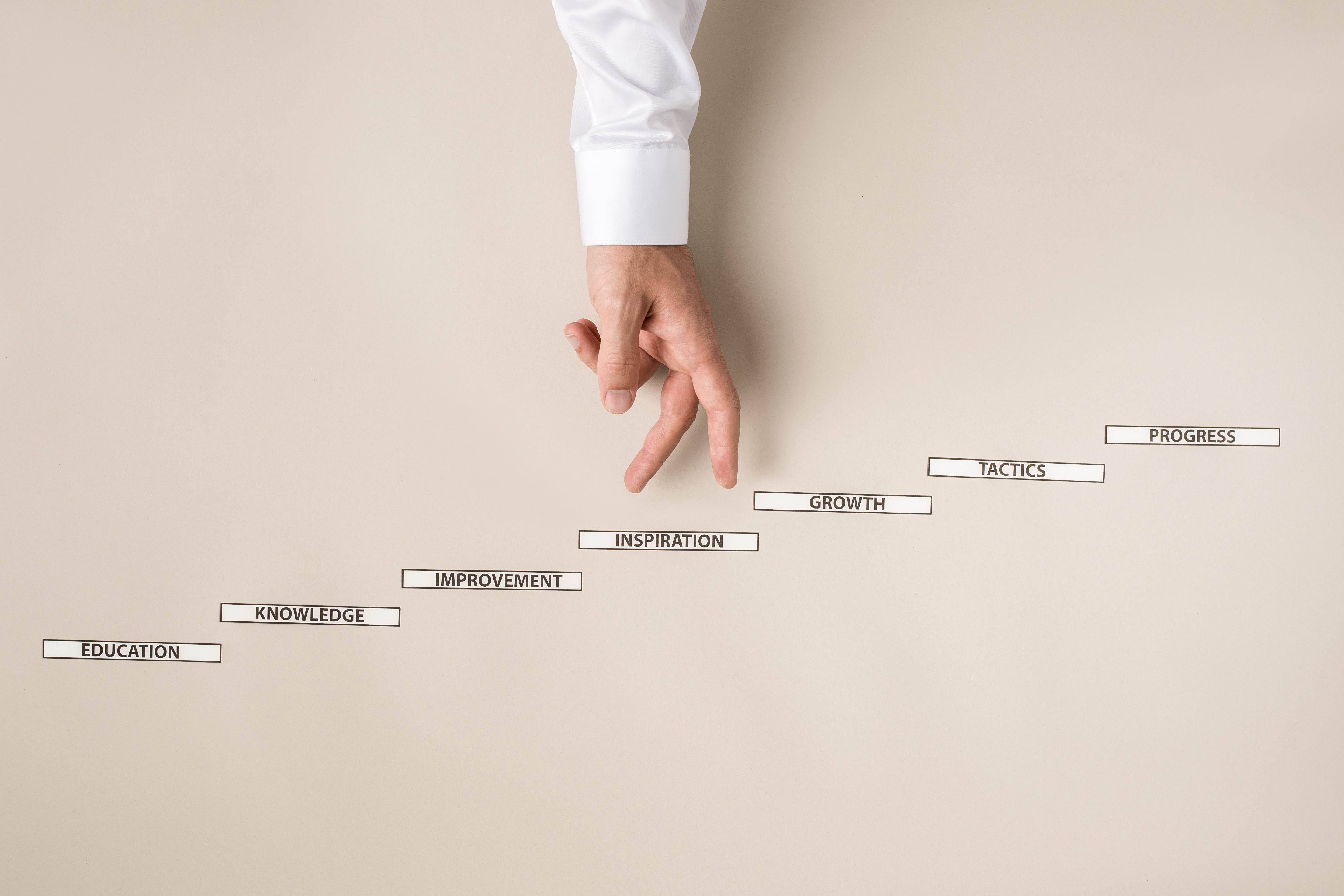
Decoding success: Business intelligence competencies
Unpacking core competencies for success in business intelligence
Dr Richard Dune
24-02-2024
In the dynamic and often unpredictable business world, success is more than just a matter of academic knowledge or technical expertise. It's a multifaceted tapestry woven from various core competencies that define true business intelligence. Daniel Goleman, a renowned psychologist and author, posits that cognitive astuteness, technical skills, and emotional intelligence are the pillars that uphold the edifice of business success. This blog delves into these competencies, exploring how they interplay to create a robust framework for business acumen.
Cognitive astuteness - The strategic thinker's edge
Cognitive astuteness refers to understanding and navigating complex situations, making strategic decisions, and solving problems efficiently.
- Critical thinking - At its core, cognitive astuteness is about critical thinking. It’s the ability to analyse information objectively, evaluate different perspectives, and arrive at a well-reasoned conclusion.
- Strategic planning - This competency involves seeing the bigger picture, setting long-term goals, and formulating plans to achieve them. It's about understanding market trends, identifying opportunities, and mitigating risks.
- Innovative problem solving - Innovative problem-solving is a hallmark of cognitive astuteness. It involves thinking creatively to find unique solutions to complex challenges, a crucial skill in an ever-evolving business landscape.

Image by dvatri via Envato Elements

Image by wosunan via Envato Elements
Technical skills - The pragmatic backbone of business
In business intelligence, these skills are essential for understanding and managing the operational aspects of a business.
- Industry knowledge - A deep understanding of the industry, including its trends, challenges, and dynamics, is fundamental. This knowledge allows for better strategic decisions and effective management.
- Data analysis and management - In an age where data is king, the ability to analyse and interpret data is crucial. It helps businesses understand their performance, customer preferences, and market trends.
- Technological proficiency - With technology driving business innovation, proficiency in relevant technological tools and platforms is indispensable. It enables businesses to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and stay competitive.
Emotional intelligence - The human factor in business
Goleman asserts that EI is as important, if not more, than cognitive ability in achieving business success.
- Self-awareness and self-regulation - This involves understanding one's emotions, strengths, weaknesses, and the impact of one's actions on others. Self-regulation pertains to managing emotions and impulses effectively.
- Empathy - Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. This translates to better customer relations, improved team dynamics, and effective leadership in business.
- Social skills - Strong social skills enable effective communication, conflict resolution, and strong professional relationships. They are essential for leadership, teamwork, and customer engagement.

Image by sofiiashunkina via Envato Elements

Image by tehcheesiong via Envato Elements
Integrating competencies for business excellence
The true power of these competencies lies in their integration. Cognitive astuteness enables strategic thinking and problem-solving, technical skills ensure operational efficiency and innovation, and emotional intelligence fosters leadership and collaborative work environments. Together, they form a holistic skill set that drives business success.
Developing core competencies of business intelligence
- Continuous learning - The business world constantly evolves, and staying up-to-date with industry knowledge, technical advancements, and best practices is essential.
- Training and development - Regular training sessions, workshops, and professional development courses can help hone these core competencies.
- Mentorship and coaching - Learning from experienced mentors and coaches can provide valuable insights and guidance in developing these skills.
- Practical application - Applying these competencies in real-world scenarios is crucial for development. It involves taking on challenging projects, leading teams, and making strategic decisions.

Image by zamrznutitonovi via Envato Elements

Image by fauziEv8 via Envato Elements
Challenges in cultivating business intelligence
Developing these competencies is not without its challenges. It requires a commitment to lifelong learning, openness to feedback, and the willingness to step out of one’s comfort zone. Additionally, balancing these skills in a way that aligns with one's personal strengths and business needs can be a complex task.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the core competencies of business intelligence – cognitive astuteness, technical skills, and emotional intelligence – are the cornerstones of success in the business world. These skills transcend traditional academic knowledge, offering a more comprehensive approach to understanding and navigating the complex landscape of modern business.
By cultivating these competencies, individuals and organisations can build a strong foundation for sustained success and growth. As Goleman eloquently puts it, in the realm of business, intelligence is not just about what you know but how you apply what you know in a strategic, pragmatic, and empathetic manner.

Image by sofiiashunkina via Envato Elements
In the dynamic and often unpredictable business world, success is more than just a matter of academic knowledge or technical expertise. It's a multifaceted tapestry woven from various core competencies that define true business intelligence. Daniel Goleman, a renowned psychologist and author, posits that cognitive astuteness, technical skills, and emotional intelligence are the pillars that uphold the edifice of business success. This blog delves into these competencies, exploring how they interplay to create a robust framework for business acumen.
Cognitive astuteness - The strategic thinker's edge

Image by dvatri via Envato Elements
Cognitive astuteness refers to understanding and navigating complex situations, making strategic decisions, and solving problems efficiently.
- Critical thinking - At its core, cognitive astuteness is about critical thinking. It’s the ability to analyse information objectively, evaluate different perspectives, and arrive at a well-reasoned conclusion.
- Strategic planning - This competency involves seeing the bigger picture, setting long-term goals, and formulating plans to achieve them. It's about understanding market trends, identifying opportunities, and mitigating risks.
- Innovative problem solving - Innovative problem-solving is a hallmark of cognitive astuteness. It involves thinking creatively to find unique solutions to complex challenges, a crucial skill in an ever-evolving business landscape.
Technical skills - The pragmatic backbone of business

Image by wosunan via Envato Elements
In business intelligence, these skills are essential for understanding and managing the operational aspects of a business.
- Industry knowledge - A deep understanding of the industry, including its trends, challenges, and dynamics, is fundamental. This knowledge allows for better strategic decisions and effective management.
- Data analysis and management - In an age where data is king, the ability to analyse and interpret data is crucial. It helps businesses understand their performance, customer preferences, and market trends.
- Technological proficiency - With technology driving business innovation, proficiency in relevant technological tools and platforms is indispensable. It enables businesses to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and stay competitive.
Emotional intelligence - The human factor in business

Image by sofiiashunkina via Envato Elements
Goleman asserts that EI is as important, if not more, than cognitive ability in achieving business success.
- Self-awareness and self-regulation - This involves understanding one's emotions, strengths, weaknesses, and the impact of one's actions on others. Self-regulation pertains to managing emotions and impulses effectively.
- Empathy - Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others. This translates to better customer relations, improved team dynamics, and effective leadership in business.
- Social skills - Strong social skills enable effective communication, conflict resolution, and strong professional relationships. They are essential for leadership, teamwork, and customer engagement.
Integrating competencies for business excellence

Image by tehcheesiong via Envato Elements
The true power of these competencies lies in their integration. Cognitive astuteness enables strategic thinking and problem-solving, technical skills ensure operational efficiency and innovation, and emotional intelligence fosters leadership and collaborative work environments. Together, they form a holistic skill set that drives business success.
Developing core competencies of business intelligence

Image by zamrznutitonovi via Envato Elements
- Continuous learning - The business world constantly evolves, and staying up-to-date with industry knowledge, technical advancements, and best practices is essential.
- Training and development - Regular training sessions, workshops, and professional development courses can help hone these core competencies.
- Mentorship and coaching - Learning from experienced mentors and coaches can provide valuable insights and guidance in developing these skills.
- Practical application - Applying these competencies in real-world scenarios is crucial for development. It involves taking on challenging projects, leading teams, and making strategic decisions.
Challenges in cultivating business intelligence

Image by fauziEv8 via Envato Elements
Developing these competencies is not without its challenges. It requires a commitment to lifelong learning, openness to feedback, and the willingness to step out of one’s comfort zone. Additionally, balancing these skills in a way that aligns with one's personal strengths and business needs can be a complex task.
Conclusion

Image by sofiiashunkina via Envato Elements
In conclusion, the core competencies of business intelligence – cognitive astuteness, technical skills, and emotional intelligence – are the cornerstones of success in the business world. These skills transcend traditional academic knowledge, offering a more comprehensive approach to understanding and navigating the complex landscape of modern business.
By cultivating these competencies, individuals and organisations can build a strong foundation for sustained success and growth. As Goleman eloquently puts it, in the realm of business, intelligence is not just about what you know but how you apply what you know in a strategic, pragmatic, and empathetic manner.
Related blog articles
View all
What is the difference between online learning and e-learning?
Related blog articles
View all
What is the difference between online learning and e-learning?

References and resources
Goleman, D. (2006) ‘Business Intelligence’. Business: The Ultimate Resource. Basic Books.
Goleman, D. (2006). Social Intelligence: The New Science of Human Relationships. Bantam.
Goleman, D. (2002) Primal Leadership: Realising the Power of Emotional Intelligence. Harvard Business School Press.
About The Mandatory Training Group
The Mandatory Training Group is one of the leading UK providers of CPDUK-accredited statutory and mandatory training, continuing professional development (CPD) courses, eLearning software and workforce development solutions for all sectors.
By making things simple and designing interactive e-learning content, we can provide meaningful training programs at all levels and enhance the capacity and resilience of individuals and organisations.
Click here to see our wide range of accredited business compliance courses and training programmes.

References and resources

Goleman, D. (2006) ‘Business Intelligence’. Business: The Ultimate Resource. Basic Books.
Goleman, D. (2006). Social Intelligence: The New Science of Human Relationships. Bantam.
Goleman, D. (2002) Primal Leadership: Realising the Power of Emotional Intelligence. Harvard Business School Press.
About The Mandatory Training Group

The Mandatory Training Group is one of the leading UK providers of CPDUK-accredited statutory and mandatory training, continuing professional development (CPD) courses, eLearning software and workforce development solutions for all sectors.
By making things simple and designing interactive e-learning content, we can provide meaningful training programs at all levels and enhance the capacity and resilience of individuals and organisations.
Click here to see our wide range of accredited business compliance courses and training programmes.
Contact us
Complete the form below to start your ComplyPlus trial and transform your regulatory compliance solutions.