You have no items in your shopping basket.
Mon - Fri 9AM - 5PM
024 7610 0090
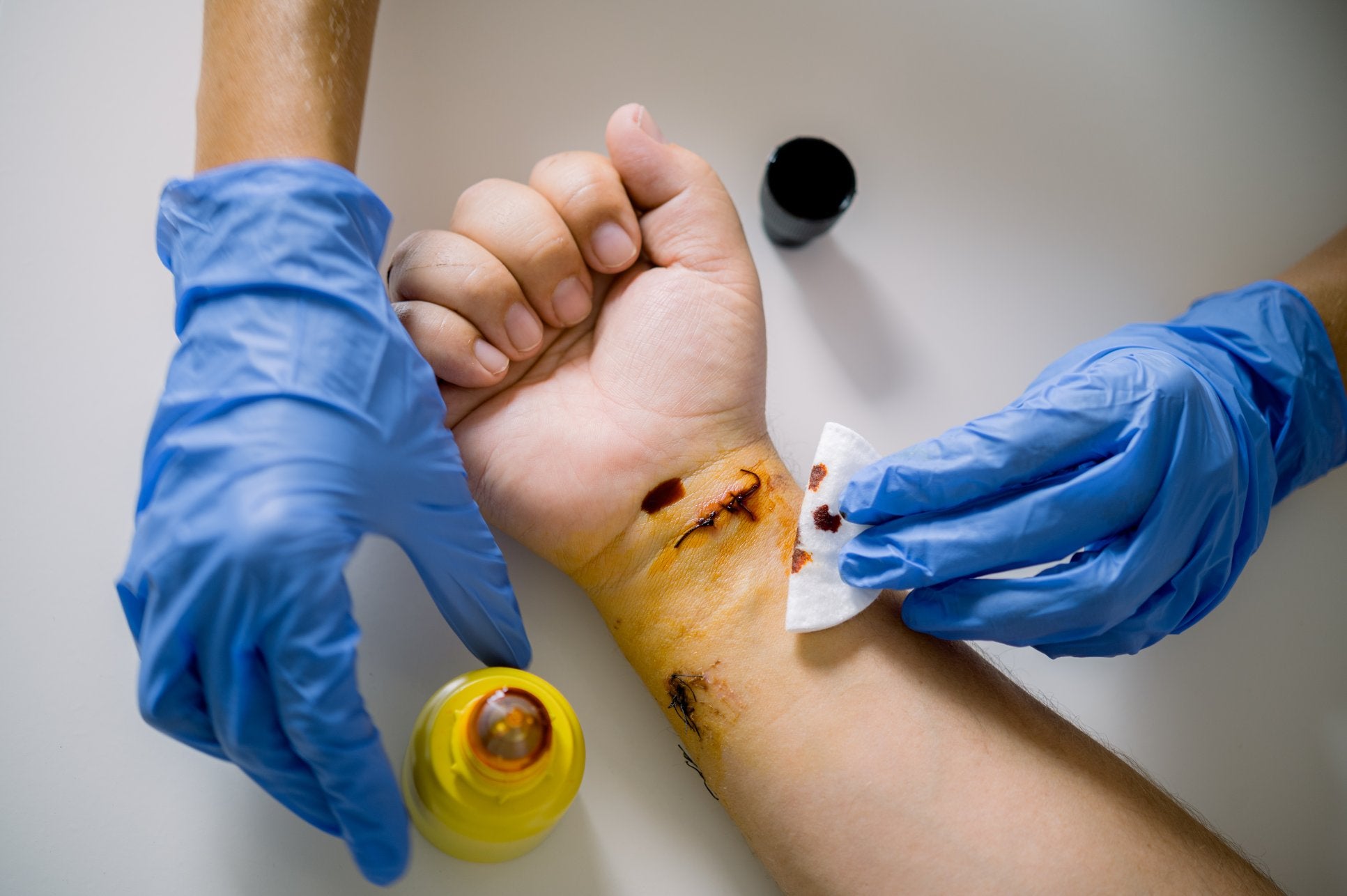
First aid treatment for a penetrating injury - ComplyPlus LMS™ - The Mandatory Training Group UK -
Penetrating injuries can occur unexpectedly and often demand immediate attention. Understanding how to administer first aid in such situations is not just valuable; it can be life-saving. In this article, we delve into the essential aspects of providing first aid treatment for penetrating injuries, highlighting key facts, legislation, regulations, and best practices to ensure the safety of both victims and responders. #FirstAidTraining
Ensuring safety: first aid treatment for penetrating injuries
Dive into the world of life-saving expertise with our comprehensive guide to mandatory training for first aid treatment for penetrating injuries. Explore accredited online courses tailored for healthcare professionals, covering essential skills such as bleeding control, tourniquet application, and best practices in emergency response. With a focus on compliance with Health and Safety (First-Aid) Regulations 1981 and Resuscitation Council UK guidelines, our training empowers individuals to confidently address penetrating injuries in any setting. Join us on ComplyPlus LMS™ for CPD accredited courses, ensuring preparedness and proficiency in the critical moments that matter most. #PenetratingInjury
The aim of this mandatory training for first aid treatment for a penetrating injury blog is to equip readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively respond to penetrating injuries in various settings. It aims to raise awareness about the importance of proper first aid treatment and to promote a culture of safety and preparedness among healthcare professionals and individuals alike. #OnlineTraining
By the end of this blog, readers should be able to:

Enhance your skills with our CPD accredited first aid eLearning courses for healthcare professionals
Sign up for our online first aid training to learn best practices in penetrating injury treatment
Click here for comprehensive workplace first aid training on ComplyPlus LMS™
Identifying penetrating injuries is crucial for initiating prompt treatment. Signs may include visible wounds, bleeding, and the presence of foreign objects lodged in the body. #EmergencyResponse
Discover our range of CPD accredited first aid courses for healthcare workers
Employers have a legal obligation to provide adequate first aid training to employees, including specific guidance on responding to penetrating injuries. Regular training sessions and drills can enhance preparedness and ensure a swift and effective response in emergencies. #ResuscitationCouncilUK
Get certified in first aid for penetrating injuries with our online CPD accredited courses
Learn tourniquet techniques and bleeding control with our accredited eLearning courses
In emergencies involving penetrating injuries, every second counts. By understanding the signs, implementing immediate actions, and receiving proper training, individuals can significantly improve the chances of positive outcomes for victims. Let's commit to prioritising first aid preparedness and safety in our communities.
Click here to explore accredited first aid courses and equip yourself with the knowledge and skills to respond effectively to emergencies. Together, we can make a difference in saving lives. #TheMandatoryTrainingGroup
Disclaimer: This blog is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always seek professional medical assistance in emergency situations.
Rose has dedicated over 15 years to improving health and social care quality through practice, targeted education and training. Her extensive experience includes working with older adults, individuals with mental health conditions, and people with autism and learning disabilities.
Mandatory training for first aid treatment for penetrating injuries in UK health and social care settings is crucial for ensuring prompt and effective response in emergencies. These courses cover key aspects such as recognising penetrating injuries, controlling bleeding, and stabilising victims. Compliance with Health and Safety (First-Aid) Regulations 1981 and Resuscitation Council UK guidelines is emphasised. Accredited training programs equip participants with necessary skills, including the use of tourniquets and wound packing techniques. Regular training sessions and drills enhance preparedness, fulfilling legal obligations and promoting a safe environment for both employees and service users. #SafetySkills
Become a first aid expert with our accredited eLearning courses for healthcare professionals
Online mandatory training for first aid treatment for penetrating injuries in UK health and social care settings offers accessible and comprehensive instruction. These courses cover vital aspects such as identifying penetrating injuries, applying pressure to control bleeding, and stabilising victims. Compliance with Health and Safety (First-Aid) Regulations 1981 and Resuscitation Council UK guidelines is emphasised. Accredited e-learning programs provide flexible learning opportunities, enabling participants to gain essential skills at their own pace. Regular assessments ensure knowledge retention and competence. Online training fulfils legal obligations while promoting a culture of safety and preparedness among healthcare professionals in diverse settings. #BleedingControl
Start your journey to becoming a certified first aider with our online training courses
Mandatory training for first aid treatment for penetrating injuries through e-learning courses is crucial in health and social care settings for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures accessibility, allowing healthcare professionals to access training anytime, anywhere, catering to busy schedules and remote work arrangements. Secondly, e-learning courses offer consistency in content delivery and assessment, ensuring that all participants receive standardised training regardless of location or instructor. Thirdly, these courses facilitate cost-effectiveness by reducing the need for physical facilities and travel expenses associated with traditional training methods. Finally, e-learning promotes ongoing learning and skill development through regular updates and refresher modules, enhancing preparedness and response capabilities in emergencies within the healthcare sector. #ProfessionalDevelopment
Access free mandatory training for first aid treatment for a penetrating injury on ComplyPlus LMS™
The Mandatory Training Group is a leading UK provider of accredited mandatory training for first aid treatment for a penetrating injury eLearning courses and training available on ComplyPlus LMS™:
Recommended Courses:
Master first aid for healthcare workers with our accredited eLearning courses.
Here are 25 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about mandatory training for first aid treatment for a penetrating injury:
Mandatory training covers essential skills and knowledge required to respond effectively to penetrating injuries, including controlling bleeding and stabilising victims.
It ensures healthcare professionals are equipped to provide immediate and effective care, potentially saving lives in emergencies.
Health and Safety (First-Aid) Regulations 1981 outline legal requirements for first aid provision in the workplace.
CPDUK certification ensures courses meet high standards of quality and compliance with professional guidelines.
ComplyPlus LMS™ offers a user-friendly platform for accessing and completing courses at one's own pace, facilitating flexible learning.
Courses cover recognising penetrating injuries, controlling bleeding, and stabilising victims, among other essential skills.
Regular refresher courses are recommended to maintain skills and stay updated on best practices.
Yes, industries like healthcare and construction may have additional first aid requirements tailored to their risks and needs.
Tourniquets may be used as a last resort to control severe bleeding in limb injuries.
By providing adequate training, resources, and ensuring first aid kits are well-stocked and accessible.
Assess personal safety, identify hazards, and evaluate the condition of the injured person.
Signs include visible wounds, pooling blood, and signs of shock such as pale skin and rapid pulse.
Apply direct pressure to the wound using a sterile dressing or clean cloth.
Visit our website and select the desired course to enrol and start learning.
Yes, we offer enhanced dental CPD courses covering first aid requirements within the dental environment.
Keep the injured person calm and reassure them while continuing to monitor their condition.
Yes, CPDUK accreditation ensures courses provide CPD credits for professional development.
Through regular assessments, quizzes, and interactive learning materials.
Leave objects in place and apply pressure around them to control bleeding.
Place them in the recovery position and monitor their breathing and condition until help arrives.
Through a variety of multimedia content including videos, simulations, and written materials.
Yes, ComplyPlus LMS™ allows access from desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones for convenience.
Posters, leaflets, and training sessions can all help raise awareness and encourage preparedness.
Participate in regular training sessions, drills, and stay informed about new developments in first aid practices.
Visit our website or contact our support team for further assistance and guidance. #WorkplaceFirstAid
Train the trainer with our online courses for mandatory first aid treatment
Choose ComplyPlus LMS™ for accredited mandatory training in first aid for penetrating injuries with The Mandatory Training Group UK. Our user-friendly platform offers flexible learning, ensuring you gain essential skills conveniently. Access CPD accredited courses anytime, anywhere, and enhance your preparedness to respond effectively in emergencies. Take the next step in your professional development and prioritise safety. Enrol now on ComplyPlus LMS™ for mandatory training in first aid treatment for penetrating injuries. Your skills could save lives. Don't wait, act now! #DentalFirstAid
Stay compliant with Health and Safety (First-Aid) Regulations 1981 with our online courses
Complete the form below to start your ComplyPlusTM trial and
transform your regulatory compliance solutions.
← Older Post Newer Post →
0 comments